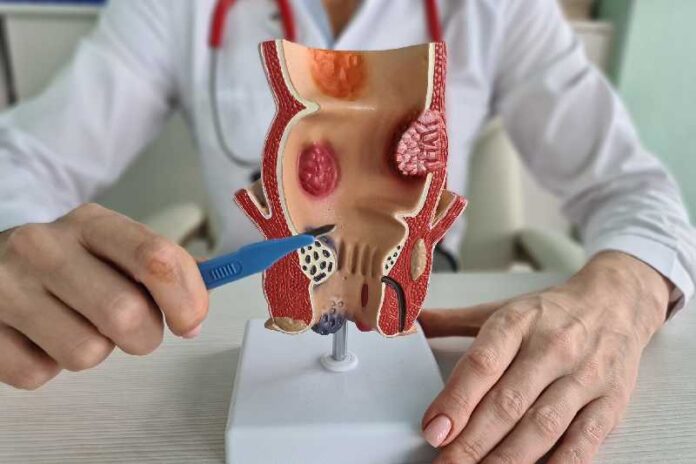
If you are feeling any discomfort or pain especially when pressure is applied to your anal region, then there is a chance that the veins in this area have become swollen.
These engorged veins and abnormal growth underneath the skin outside the anus or surrounding the inner part of the rectum are called haemorrhoids. Learn more about the causes of haemorrhoids and how to remove them in this article.
Causes of haemorrhoids
Haemorrhoids can be caused by a lot of factors. Your risk of developing them increases as you age and you may also have them if one of your close blood relatives had them. They can also be due to these factors:
- Being overweight or obese
- Chronic constipation or diarrhoea
- Doing physical activities that cause you to strain, such as heavy lifting
- Eating foods that are low in fibre
- Extreme effort when pushing out bowel
- Pregnancy in women
These factors affect the flow of blood in the lower rectum and cause the veins to swell.
Signs and symptoms of haemorrhoids
The signs and symptoms of haemorrhoids include:
- Blood in stool or on the toilet paper after bowel movement
- Itching and pain in the anal area
- Lumps surrounding the anus
Haemorrhoids typically resolve on their own, but if the symptoms worsen over time, then you should get checked by a doctor. There are other diseases that also cause rectal bleeding, so it is best that you get checked by a doctor and undergo necessary tests to get an accurate diagnosis and the right treatment plan.
Haemorrhoids that are left untreated can lead to complications like:
- Anaemia
- Clotting of blood
- Strangulated hemorrhoid
Diagnosing haemorrhoids
Diagnosing haemorrhoids can be done by your doctor by doing the following:
- General consultation – Your doctor asks about your family medical history as well as information about your symptoms, like when they started and how often you feel any discomfort.
- Physical inspection – Your doctor inserts a gloved finger that is lubricated into your rectum to feel any signs of swollen vein or abnormal growths.
- Visual examination – This procedure uses a medical device that is equipped with a tiny light and camera that is inserted into the rectum and lower part of the large intestine to check for blood clots, swelling veins, or lumps.
Removal of haemorrhoids
Once the doctor has confirmed the existence of haemorrhoids, a plan can be made to treat it.
Home treatments can be done for mild haemorrhoids. Below are ways that can bring relief and manage the discomfort caused by haemorrhoids:
- Applying of cold compress to the affected area
- Drinking lots of water
- Eating more fibrous foods
- Soaking in warm baths
- Taking fibre supplements
- Using medicated suppositories and pads
Haemorrhoids that are more severe, such as prolapsed and thrombosed haemorrhoids, will need the intervention of medical procedures to remove them.
- Prolapsed haemorrhoids – This occurs when an internal hemorrhoid protrudes out of the anus. It is painful during bowel movement or when sitting down. Internal haemorrhoids are graded according to the severity of their prolapse:
| Grade | Severity of prolapse |
| 1 | No signs of prolapse |
| 2 | Prolapse is observed, but can retreat without intervention |
| 3 | Prolapse that needs intervention to be pushed back into the rectum |
| 4 | Prolapse that cannot be pushed back in despite intervention |
- Thrombosed haemorrhoids – This occurs when a prolapsed hemorrhoid develops a blood clot inside.
The treatment for prolapsed and thrombosed haemorrhoids will depend on its type and grade. The most common procedures used to treat these conditions are:
- Coagulation
- Rubber band ligation
- Sclerotherapy
- Surgery
Coagulation may use an infrared light, a laser, or heat to dissolve a hemorrhoid.
Rubber band ligation, otherwise known as banding, uses one or two small rubber bands that are tightly placed around the haemorrhoids to cut off blood circulation and shrink the swelling. The hemorrhoid is expected to fall off naturally along with the rubber bands in a week.
Sclerotherapy is done using chemicals that are administered into the growth. The chemicals cause the blood vessels in the haemorrhoids to shrink and remove it.
Surgery is usually the last resort for hemorrhoid removal and is used for external thrombosed haemorrhoids. A minor surgery involves removing the hemorrhoid and wound draining. Complete hemorrhoid tissue removal, also known as full hemorrhoidectomy, is performed for haemorrhoids that are prolapsed and are severe (grade 3 and 4 haemorrhoids).
Prevention of haemorrhoids
Haemorrhoids can be prevented and their symptoms can be reduced. Here are some ways to do it:
- Do not sit for long periods of time – The weight placed on the anal region while sitting for a long time can heighten the pressure in the veins and cause them to swell.
- Get regular exercise – Keeping your weight at a healthy level minimizes the pressure placed on the lower part of your body, especially when sitting.
- Pass soft stools – Stools that are hard can be difficult to expel. Putting constant pressure as you push them out of your system can cause strain to your rectum, causing the veins in this area to swell. To avoid this, include more whole grains, fruits, and vegetables to your diet. Foods that are high in fibre make soft stools. Likewise, drink a lot of water and healthy fluids.
- Avoid straining when passing stools – Pressure builds up more when you hold your breath and strain during bowel movement. Practice exhaling air as you push out your stools to avoid pressure build up.
- Do not stop the urge to pass stools – Stopping the urge to release bowel can make your stool dry and be more difficult to pass.
Consult with a doctor
Do not wait for your symptoms to worsen before consulting with a doctor. If you suspect that you have haemorrhoids, book a consultation with a gastroenterologist. In Singapore, you can reach out to Gastrohealth Clinic to have the health of your gastrointestinal region checked.
Once you have booked your initial appointment, prepare for your consultation by:
- Listing all your signs and symptoms
- Making a diary of your diet as well as bowel habits
- Writing down questions to ask your doctor
You can also start making changes to your lifestyle, such as tweaking your diet, prior to your doctor’s consultation in order to relieve your symptoms.





